VOX is family a post-quantum signature algorithms submitted to NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Project on May 31th, 2023. It has been designed by: Benoît Cogliati, Jean-Charles Faugère, Pierre-Alain Fouque, Louis Goubin, Robin Larrieu, Gilles Macario-Rat, Brice Minaud and Jacques Patarin.
The VOX family includes a specific instantiation called “VOX-F” (or Full VOX, nicknamed “FOX”) that does not use the QR technique and allows to obtain easier security arguments.
Due to attacks on the QR technique (see the Updates/News section below for more details), FOX is at present our main version of VOX.
VOX/FOX is based on multivariate cryptography (UOV problem and the problem of solving algebraic equations).
Thanks to the ^+ trick, it is possible to follow two opposite strategies.
First, one can use this security increase to reduce parameter sizes, and try to use more aggressive optimizations.
Second, one can keep a secure UOV instance, and then further enhance its security with the ˆ+ variant.
In the design of FOX, we chose the second approach. Thus, FOX has very conservative parameters. Moreover, we selected our parameter sets so that the cost of canceling the added random polynomials for two public equations is the same as breaking the underlying UOV problem.
FOX is a UOV-based hash-and-sign signature scheme from the Multivariate Quadratic (MQ) family, built around a new variant proposed by Faugère, Macario-Rat, Patarin, and Perret under the name UOVˆ+ [pdf].
While the quadratic forms of a UOV public key have a large common isotropic subspace, which is unusual for a random quadratic system, UOVˆ+ adds a small number of uniformly random quadratic forms to the public keys to hide this subspace. For the same parameter sizes, UOVˆ+ is then more secure than the corresponding UOV instance.
Hence, FOX can keep all benefits of UOV, such as small signature sizes, fast signature generation, and extremely fast verification, while also offering an additional security guarantee.
As an illustration, the size of the signature is only 124 bytes for FOX-I with security level I for public key size 50.3 Kbytes. The verification time is very good and we can sign 277 messages per second if the secret key is decompressed.
We define the parameters for each variant of FOX according to the three security levels defined by the NIST.
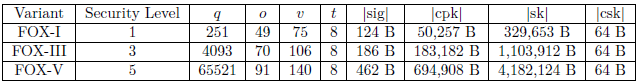
The size of the signature (|sig|), the public key (|cpk|), the secret key (|sk|) and the compressed secret key (|csk|) are expressed in bytes.
Using the reference implementation on a common laptop computer (11th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-1185G7 @ 3.00GHz , TurboBoost enabled), FOX achieves the following performance:
| Level | Keygen | Sign | Sign [cached SK] | Verify | Verify [cached PK] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOX-I | 13.25ms / 34339422 c | 5.07ms / 13153496 c | 4.34ms / 11252449 c | 1.32ms / 3423563 c | 0.06ms / 168437 c |
| FOX-III | 51.53ms / 133580482 c | 7.90ms / 20484823 c | 4.94ms / 12798162 c | 6.83ms / 17712780 c | 0.13ms / 330683 c |
| FOX-V | 562.99ms / 1459339050 c | 45.61ms / 118235215 c | 40.51ms / 105005378 c | 16.70ms / 43293387 c | 2.98ms / 7737203 c |
All the timings are given in milliseconds (ms) and in cycles (c)
Using AVX2 implementation on a common laptop computer (11th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-1185G7 @ 3.00GHz , TurboBoost enabled), FOX achieves the following performance:
| Level | Keygen | Sign | Sign [cached SK] | Verify | Verify [cached PK] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOX-I | 11.49ms / 29771117 c | 4.24ms / 11000844 c | 3.61ms / 9362493 c | 1.05ms / 2723488 c | 0.04ms / 106974 c |
| FOX-III | 48.33ms / 125270708 c | 7.27ms / 18834197 c | 4.61ms / 11946513 c | 6.37ms / 16516109 c | 0.13ms / 348334 c |
| FOX-V | 166.38ms / 431306224 c | 29.28ms / 75903168 c | 23.51ms / 60961314 c | 10.40ms / 26965333 c | 0.59ms / 1532779 c |
All the timings are given in milliseconds (ms) and in cycles (c)
The verification time is very good and we can sign 277 messages per second if the secret key is decompressed and 236 otherwise.
(Version 2024-05-17): .
(Version 2023-07-28): .
(Version 2023-05-31): .